Page 15 - Highlights of Napcon 2021
P. 15
New ATS/IDSA Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Guideline: More Micro, Less Macrolide, No HCAP
Dr. Ajeet Singh
Senior Consultant, Division of Allergy & Pulmonary Medicine
SMS Medical College
Jaipur
Dr. Ajeet Singh walked through the 2019 American Thoracic Society (ATS)/Infectious Diseases Society of America
(IDSA) guideline on community-acquired pneumonia (CAP).
Dr. Singh wanted to see how the guideline can help integrate the assessment of clinical severity and risk for multidrug
resistance (MDR) into the management of CAP. His other interest was identifying indications for obtaining sputum
and blood cultures, nasal methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus polymerase chain reaction (MRSA PCR), and
additional diagnostic studies.
He quickly covered global epidemiology, risk factors, and the etiology of CAP. In CAP, non-microbial etiology is the
most common. He also discussed the pneumonia severity index for assessing the class of risk. He explained the CURB-
65, SCAP, and SMART COP and the IDSA/ATS 2007 Scores. According to Dr. Singh, the new American Thoracic
Society (ATS) 2019 guidelines differs from old guidelines for better management and good adherence to treatment.
ATS 2019 was modified to classify pneumonia, diagnosis, and treatment of CAP. The new guideline includes only
CAP and ventilator or hospital-associated pneumonia (VAP/HAP) but not healthcare-associated pneumonia (HCAP).
Currently, blood and sputum is recommended in patients with severe disease as well as in all inpatients treated for
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or pseudomonas. The use of procalcitonin is not recommended
to determine the need for initial antimicrobial therapy. Corticosteroids might be used only in patients with refractory
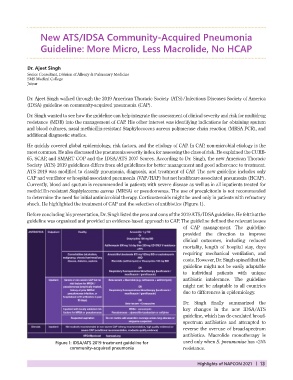
shock. He highlighted the treatment of CAP and the selection of antibiotics (Figure 1).
Before concluding his presentation, Dr. Singh listed the pros and cons of the 2019 ATS/IDSA guideline. He felt that the
guideline was organized and provided an evidence-based approach to CAP. The guideline defined the relevant issues
of CAP management. The guideline
provided the direction to improve
clinical outcomes, including reduced
mortality, length of hospital stay, days
requiring mechanical ventilation, and
costs. However, Dr. Singh opined that the
guideline might not be easily adaptable
to individual patients with unique
antibiotic intolerance. The guideline
might not be adaptable to all countries
due to differences in epidemiology.
Figure 1: IDSA/ATS 2019 treatment guideline for Dr. Singh finally summarized the
community-acquired pneumonia key changes in the new IDSA/ATS
guideline, which has de-escalated broad-
spectrum antibiotics and attempted to
reverse the overuse of broad-spectrum
antibiotics. Macrolide monotherapy is
used only when S. pneumoniae has <25%
resistance.
Highlights of NAPCON 2021 13