Page 11 - Demo
P. 11
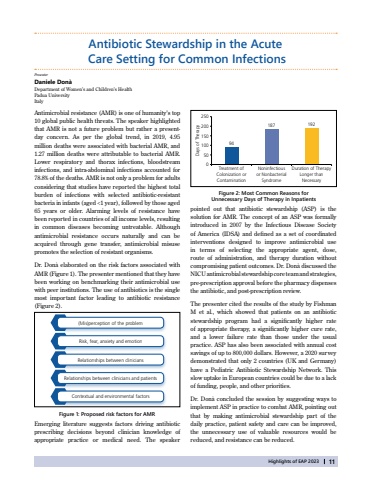
Highlights of EAP 202311Antibiotic Stewardship in the Acute Care Setting for Common InfectionsAntimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of humanity%u2019s top 10 global public health threats. The speaker highlighted that AMR is not a future problem but rather a presentday concern. As per the global trend, in 2019, 4.95 million deaths were associated with bacterial AMR, and 1.27 million deaths were attributable to bacterial AMR. Lower respiratory and thorax infections, bloodstream infections, and intra-abdominal infections accounted for 78.8% of the deaths. AMR is not only a problem for adults considering that studies have reported the highest total burden of infections with selected antibiotic-resistant bacteria in infants (aged <1 year), followed by those aged 65 years or older. Alarming levels of resistance have been reported in countries of all income levels, resulting in common diseases becoming untreatable. Although antimicrobial resistance occurs naturally and can be acquired through gene transfer, antimicrobial misuse promotes the selection of resistant organisms. Dr. Don%u00e0 elaborated on the risk factors associated with AMR (Figure 1). The presenter mentioned that they have been working on benchmarking their antimicrobial use with peer institutions. The use of antibiotics is the single most important factor leading to antibiotic resistance (Figure 2).Daniele Don%u00e0 Department of Women%u2019s and Children%u2019s HealthPadua UniversityItalyFigure 2: Most Common Reasons for Unnecessary Days of Therapy in Inpatientspointed out that antibiotic stewardship (ASP) is the solution for AMR. The concept of an ASP was formally introduced in 2007 by the Infectious Disease Society of America (IDSA) and defined as a set of coordinated interventions designed to improve antimicrobial use in terms of selecting the appropriate agent, dose, route of administration, and therapy duration without compromising patient outcomes. Dr. Don%u00e0 discussed the NICU antimicrobial stewardship core team and strategies, pre-prescription approval before the pharmacy dispenses the antibiotic, and post-prescription review.The presenter cited the results of the study by Fishman M et al., which showed that patients on an antibiotic stewardship program had a significantly higher rate of appropriate therapy, a significantly higher cure rate, and a lower failure rate than those under the usual practice. ASP has also been associated with annual cost savings of up to 800,000 dollars. However, a 2020 survey demonstrated that only 2 countries (UK and Germany) have a Pediatric Antibiotic Stewardship Network. This slow uptake in European countries could be due to a lack of funding, people, and other priorities. Dr. Don%u00e0 concluded the session by suggesting ways to implement ASP in practice to combat AMR, pointing out that by making antimicrobial stewardship part of the daily practice, patient safety and care can be improved, the unnecessary use of valuable resources would be reduced, and resistance can be reduced.Figure 1: Proposed risk factors for AMR(Mis)perception of the problemRisk, fear, anxiety and emotionRelationships between cliniciansRelationships between clinicians and patientsContextual and environmental factorsEmerging literature suggests factors driving antibiotic prescribing decisions beyond clinician knowledge of appropriate practice or medical need. The speaker 250200150100500Treatment of Colonization or ContaminationNoninfectious or Nonbacterial SyndromeDuration of Therapy Longer than NecessaryDays of Therapy94187192Presenter